Introduction
The m12 4 pin connector m12 pinout is one of the most widely used connectivity standards in industrial automation, sensors, robotics, and machine control systems. With multiple pinout configurations, color codes, and connector types available, choosing the correct M12 variant can feel overwhelming—especially when system reliability and signal integrity are on the line. This guide breaks down each connector type, pinout standard, and application to help you determine which M12 4-pin configuration best aligns with your project.
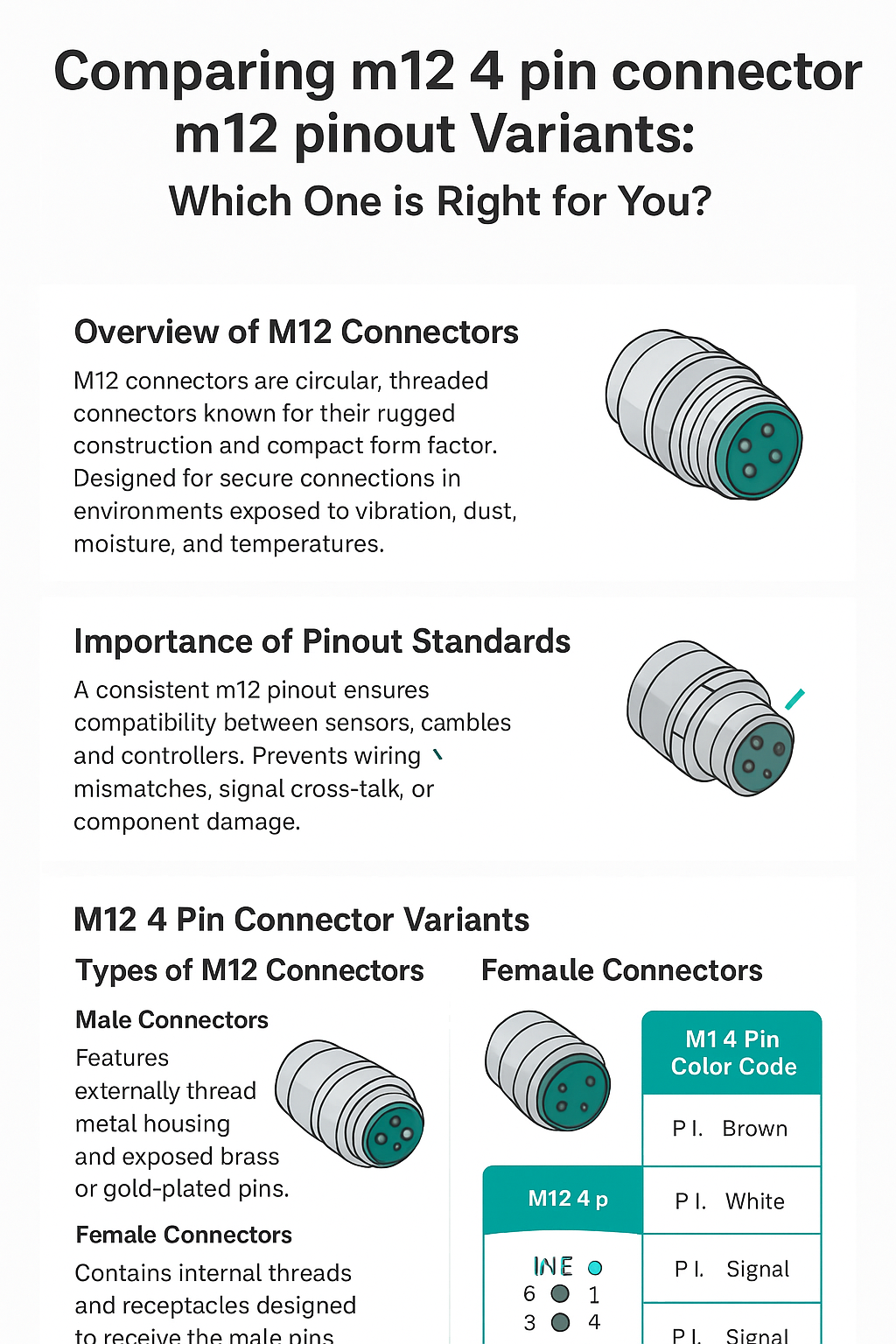
Overview of M12 Connectors
M12 connectors are circular, threaded connectors known for their rugged construction and compact form factor. They are designed to provide secure connections in environments exposed to vibration, dust, moisture, and temperature extremes. These connectors come in several coding types—such as A-coded, B-coded, D-coded, and others—each tailored to specific signal or power requirements.
Importance of Pinout Standards
A consistent m12 pinout ensures compatibility between sensors, cables, and controllers. With dozens of manufacturers producing M12 connectors, pinout standards prevent wiring mismatches, signal cross-talk, or component damage. Understanding the layout and function of each pin is crucial for proper installation and operation.
M12 4 Pin Connector Variants
The m12 4 pin connector is typically A-coded, making it ideal for DC power, sensors, actuators, and general signal transmission. Variants differ by use case, cable type, and connector configuration.
Types of M12 Connectors
Male Connectors
The m12 4 pin male connector features externally threaded metal housing and exposed brass or gold-plated pins. It is commonly found on sensor bodies and device housings.
Female Connectors
The m12 4 pin female connector contains internal threads and receptacles designed to receive the male pins. These are typically found on cable assemblies and extension cables.
Comparison of M12 4 Pin Variants
Different M12 variants offer advantages depending on environmental protection ratings, pin arrangements, cable jacket materials, and mounting styles. For example:
Overmolded cables provide better sealing than field-wireable connectors.
Panel-mount connectors are ideal for device housings.
Right-angle connectors accommodate tight installation spaces.
Understanding these differences ensures you select a connector optimized for durability and performance.
Understanding M12 Pinout
General Pinout Structure
A standard M12 4-pin A-coded connector follows a uniform pin arrangement:
Four evenly spaced pins (or sockets)
Keyed alignment notch for orientation
Standardized numbering pattern across manufacturers
Pin Configuration
For most M12 4-pin connectors, the configuration is:
Pin 1 – Brown – Positive supply (V+)
Pin 2 – White – Optional signal or data
Pin 3 – Blue – Ground (V–)
Pin 4 – Black – Signal
This universal structure ensures interchangeability between cable assemblies and devices.
Common Applications
The 4-pin M12 is commonly used in:
Proximity sensors
Encoders
Light curtains
DC power connections
Robotics
Industrial I/O blocks
M12 Color Code
M12 Cable Color Code Significance
The m12 color code helps installers quickly identify wiring assignments and avoid cross-wiring. Since many industrial systems use standardized wire colors, matching the color code to the pinout makes troubleshooting far easier.
M12 4 Pin Color Code Chart
Pin Color Typical Function
1 Brown V+ (Power)
2 White Signal/Data
3 Blue V– (Ground)
4 Black Signal/Data
This chart applies to both male and female M12 A-coded connectors.
Detailed Look at M12 Connector Pinout
M12 4 Pin Male Connector Pinout
On the male connector:
Pins protrude outward
Pin 1 usually appears at the top when aligned to the notch
Numbering follows a clockwise pattern
The male connector’s pin orientation is critical when wiring sensors or custom cable assemblies.
M12 4 Pin Female Connector Pinout
The m12 4 pin female connector pinout is the mirror image of the male connector:
Sockets accept corresponding male pins
Pin numbering follows the same alignment
Color codes remain identical
Because of its mirrored design, installers must always double-check orientation before wiring field-assembled connectors.
Use Cases for Each Type
Male M12 4-pin connectors
Typically fixed to equipment such as sensors, switches, and actuators.
Female M12 4-pin connectors
Found on cable ends for quick-disconnect functionality, enabling fast equipment swaps and modular system design.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting the correct m12 4 pin connector m12 pinout comes down to understanding your system requirements.
Factors to Consider
Application Requirements
DC power vs signal transmission
Required voltage/current rating
Signal type (analog, digital, data)
Connector Durability
IP67 or IP68 protection
Vibration resistance
Cable jacket material (PVC, PUR, TPE)
Temperature rating
For harsh industrial environments, PUR-jacketed cables and IP67+ connectors are recommended.
Final Recommendations
Summary of Options
Choose A-coded 4-pin M12 connectors for sensors, actuators, and power.
Use factory-molded cables when moisture protection is critical.
Select field-wireable connectors when custom cable lengths are needed.
Match the m12 cable color code to ensure proper wiring.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences among m12 4 pin connector m12 pinout variants ensures reliable system performance, reduced downtime, and easier installation. Whether you need a male or female connector, molded cable, or field-assembled option, following standardized pinouts and color codes guarantees compatibility across devices. With the right connector choice, your automation system will operate smoothly in even the toughest industrial environments.
Post time: December 6th 2025

 Emily2014515
Emily2014515